What are the main materials of cut-resistant gloves?

Cut-resistant gloves are essential for safety in industries like construction, glass handling, and heavy-duty work. Without the right materials, these gloves cannot provide adequate protection against cuts and abrasions.
Cut-resistant gloves are primarily made from materials like HPPE, Kevlar, steel fibers, and composite yarns. These materials are combined to achieve different levels of cut resistance.
When choosing the right gloves, understanding their materials helps buyers make informed decisions. Let’s explore these materials and standards in greater detail.
What materials are cut-resistant gloves made of?
Cut-resistant gloves are made using advanced materials designed to resist cuts while maintaining flexibility and comfort. These materials form the backbone of protective gloves used in heavy-duty industries.
The key materials used in cut-resistant gloves are high-performance polyethylene (HPPE), Kevlar, stainless steel fibers, and composite yarns.

Materials of Cut-Resistant Gloves
High-Performance Polyethylene (HPPE)
HPPE is one of the most widely used materials for cut-resistant gloves. It is lightweight yet incredibly strong. HPPE fibers provide a balance of flexibility and durability, making them suitable for tasks requiring dexterity. Additionally, these fibers are resistant to abrasions, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Kevlar
Kevlar is a synthetic fiber known for its incredible strength and heat resistance. Its durability makes it a popular choice for gloves used in industries like glass cutting and automotive work. Kevlar is also lightweight and comfortable to wear for extended periods.
Stainless Steel Fibers
Stainless steel fibers are often woven into gloves to enhance their cut resistance. These fibers create a protective barrier against sharp objects. However, gloves with stainless steel fibers may feel heavier compared to those made from HPPE or Kevlar.
Composite Yarns
Composite yarns combine multiple materials, such as Kevlar and stainless steel, to achieve higher levels of protection. These gloves are often used in heavy industrial applications where maximum cut resistance is required.
What is cut-resistant fabric made of?
Cut-resistant fabrics are made using a combination of advanced fibers and materials, engineered to withstand cuts and abrasions. These fabrics form the base for gloves and other protective gear.
Cut-resistant fabrics typically include a blend of Kevlar, HPPE, glass fibers, and sometimes nylon for added flexibility.
Understanding Cut-Resistant Fabrics in Detail
Cut-resistant fabrics are designed to perform under high stress. They often include the following components:
- Kevlar: Adds strength and durability.
- HPPE: Enhances flexibility and comfort.
- Glass Fibers: Reinforce the fabric’s cut resistance.
- Nylon: Improves the elasticity and fit of the material.
For example, fabrics used in heavy-duty gloves might have a higher concentration of glass or stainless steel fibers, whereas lightweight gloves might focus on HPPE and nylon for added dexterity.
What is the standard for cut-resistant gloves?
Cut-resistant gloves are evaluated based on internationally recognized safety standards. These standards ensure gloves provide consistent and reliable protection in various work environments.
The main standards for cut-resistant gloves are EN 388 (European Standard) and ANSI/ISEA 105 (American Standard).
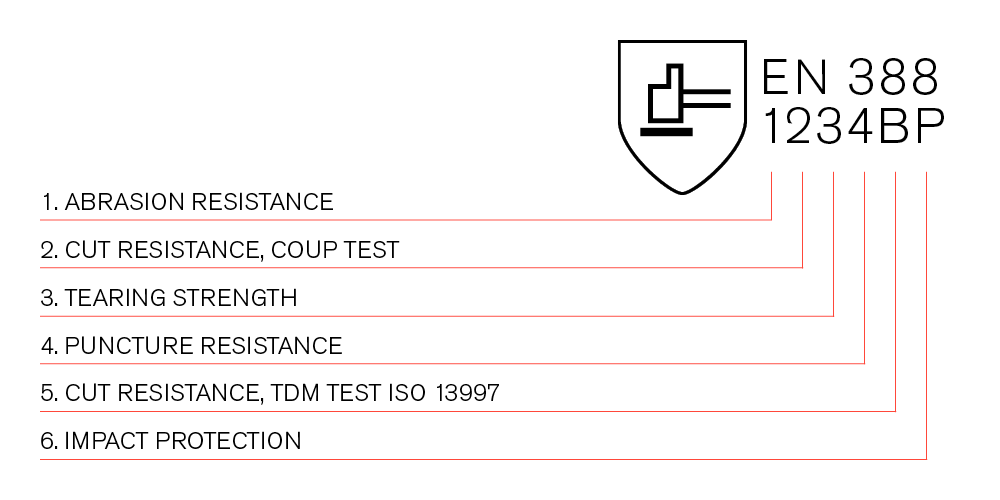
Cut-Resistance Standards
EN 388
EN 388 is the European standard for protective gloves. It rates gloves on their resistance to cuts, abrasions, tears, and punctures. The cut resistance is measured on a scale from A to F, with F being the highest level of protection.
ANSI/ISEA 105
In the United States, the ANSI/ISEA 105 standard is used to classify cut resistance. This standard assigns gloves a cut resistance score from A1 to A9, with A9 offering the highest level of protection.
Here’s a table comparing EN 388 and ANSI/ISEA 105:
| Standard | Cut Resistance Scale | Highest Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
| EN 388 | A to F | F |
| ANSI/ISEA 105 | A1 to A9 | A9 |
What are the raw materials for gloves?
The raw materials used in gloves vary based on their intended use. For cut-resistant gloves, these materials are carefully selected to provide a balance of safety, comfort, and durability.
Raw materials for gloves include HPPE, Kevlar, glass fibers, stainless steel, nylon, and sometimes natural latex or nitrile for coatings.
Types of Raw Materials for Gloves
Fibers and Yarns
- Kevlar: Provides heat and cut resistance.
- HPPE: Offers lightweight cut protection.
- Glass Fibers: Enhance durability and cut resistance.
Coatings
- Nitrile: Improves grip and chemical resistance.
- Polyurethane (PU): Provides a snug fit and dexterity.
- Latex: Offers flexibility and a strong grip.
Reinforcements
In high-performance gloves, materials like stainless steel fibers or composite yarns are added to increase strength without sacrificing flexibility.
Conclusion
Understanding the materials and standards behind cut-resistant gloves ensures you choose the right protection for your needs. Whether it’s HPPE, Kevlar, or stainless steel fibers, each material offers unique benefits tailored to specific industries.
