What is the EN388 standard for gloves?
When buying protective gloves, the “EN388 standard” often appears. But what does it mean? Understanding this standard ensures workers receive optimal safety.
The EN388 standard is a European regulation that measures protective gloves' resistance to abrasion, cuts, tearing, and punctures.
Knowing this helps you make informed purchasing decisions. Let’s dive deeper into its meaning, related EN and ISO standards, and ASTM equivalents.
What does EN 388 mean on gloves?
The EN388 mark is crucial for understanding glove safety. But what exactly does it signify?
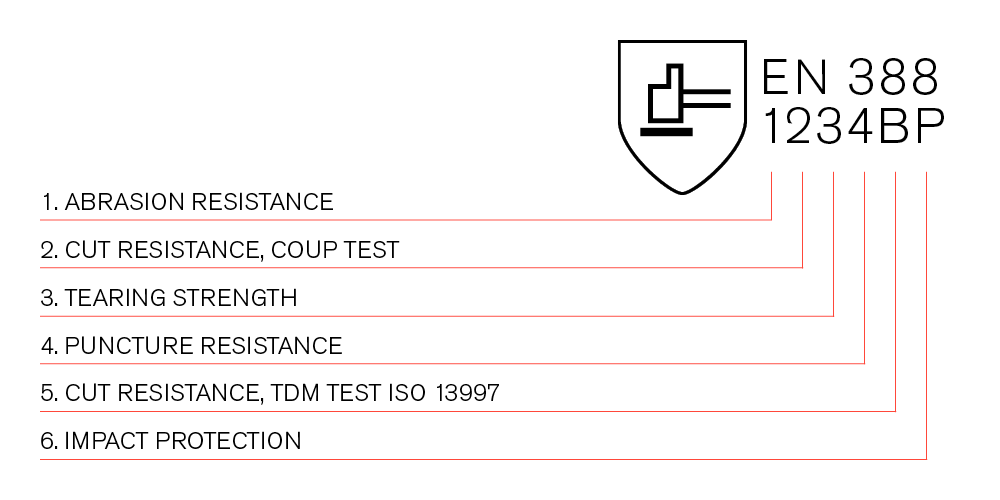
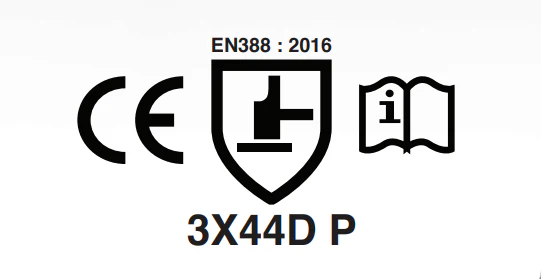
EN388 indicates a glove's performance against mechanical risks: abrasion, cut, tear, puncture, and sometimes impact resistance.
How EN388 ratings work
The EN388 standard uses numbers and letters to represent different levels of protection:
| Mechanical Risk | Testing Method | Performance Levels (1-4/5) |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Resistance | Sandpaper wear test | 1–4 |
| Cut Resistance (Coup) | Rotating blade test | 1–5 |
| Tear Resistance | Tensile strength test | 1–4 |
| Puncture Resistance | Puncture by steel probe | 1–4 |
| Cut Resistance (ISO 13997) | Straight blade test | A–F |
- Abrasion Resistance: Tested using sandpaper under pressure. Higher numbers mean better durability.
- Cut Resistance: EN388 measures two types of cuts — “Coup Test” (rotating blade) and ISO 13997 (for tougher materials).
- Tear and Puncture Resistance: Essential for environments involving sharp or rough materials.
If impact protection is tested (optional), a “P” will appear after the performance scores.
Why EN388 Matters
Choosing the correct EN388-rated glove depends on your working environment. For example:
- Construction sites require high abrasion and tear resistance.
- Glass handling needs top-level cut resistance.
Understanding the EN388 codes ensures safety and cost-efficiency in purchasing.
What is the EN number for gloves?
The EN number tells us which European standard a glove complies with. But what does it include?
The EN number for gloves refers to standards such as EN388 (mechanical risks), EN407 (heat), EN511 (cold), and EN420 (general requirements).
A breakdown of key EN numbers
There are multiple EN standards for different types of risks:
| EN Standard | Description | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| EN 388 | Mechanical risks | Abrasion, cut, tear, puncture |
| EN 407 | Thermal risks (heat & fire) | Burning, contact heat |
| EN 511 | Cold protection | Convective and contact cold |
| EN 420 | General glove requirements | Sizing, comfort, dexterity |
Each EN standard guarantees certain performance criteria. For example:
- EN407 ensures gloves protect workers from heat and flames.
- EN511 ensures protection against freezing temperatures.
When choosing gloves for your industry, always match the EN number to the work environment risks.
What are the ISO standards for gloves?
ISO standards take glove safety to a global level. So, how do they compare to EN standards?
ISO standards for gloves, such as ISO 13997, focus on cut resistance and durability to meet international safety benchmarks.
ISO 13997 and its role in EN388
ISO 13997 complements EN388’s cut resistance test by measuring:
- Blade force required to cut through glove material.
- Test results given in letters (A–F), with “F” offering the highest cut protection.
For industries handling sharp tools, like metal work or glass manufacturing, ISO 13997 ensures gloves perform reliably.
| Letter Grade | Blade Force (Newtons) | Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
| A | 2–5 | Basic protection |
| B | 5–10 | Medium protection |
| C | 10–15 | High protection |
| D | 15–22 | Strong protection |
| E | 22–30 | Very strong |
| F | ≥30 | Maximum |
By integrating ISO standards, gloves comply with broader global regulations. This allows businesses to export with confidence.
What is the ASTM standard for gloves?
The U.S. primarily uses ASTM standards for glove safety. How do they align with EN388?
ASTM standards test protective gloves for cut resistance, impact strength, and other mechanical risks to ensure worker safety.
Key ASTM Standards
ASTM standards relevant to gloves include:
| ASTM Standard | Description | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM F2992-15 | Cut resistance testing | Cut |
| ASTM D3389 | Abrasion resistance | Wear |
| ASTM F2878 | Puncture resistance | Sharp objects |
- Cut Resistance (F2992-15): This test uses a straight-edge blade under controlled force, producing consistent results.
- Abrasion Resistance (D3389): Similar to EN388, it evaluates how gloves withstand friction.
- Puncture Resistance (F2878): Measures gloves’ ability to resist punctures from hypodermic needles or probes.
Comparing ASTM and EN388
Both standards aim to protect workers. However:
- EN388 is primarily used in Europe.
- ASTM dominates the U.S. market.
When exporting gloves to the U.S., ensuring compliance with ASTM standards guarantees market acceptance.
Conclusion
The EN388 standard is vital for evaluating glove performance against mechanical risks. By understanding EN numbers, ISO standards, and ASTM equivalents, businesses can ensure they choose the right protective gloves for every industry.

One Response